Posted: September 9, 2014
Contributing Authors: C. Young, D. Yang, R. Fontaine, J. Morrison, D. James, Chad Davis and Albert Cowsky

Inside the Apple iPhone 6
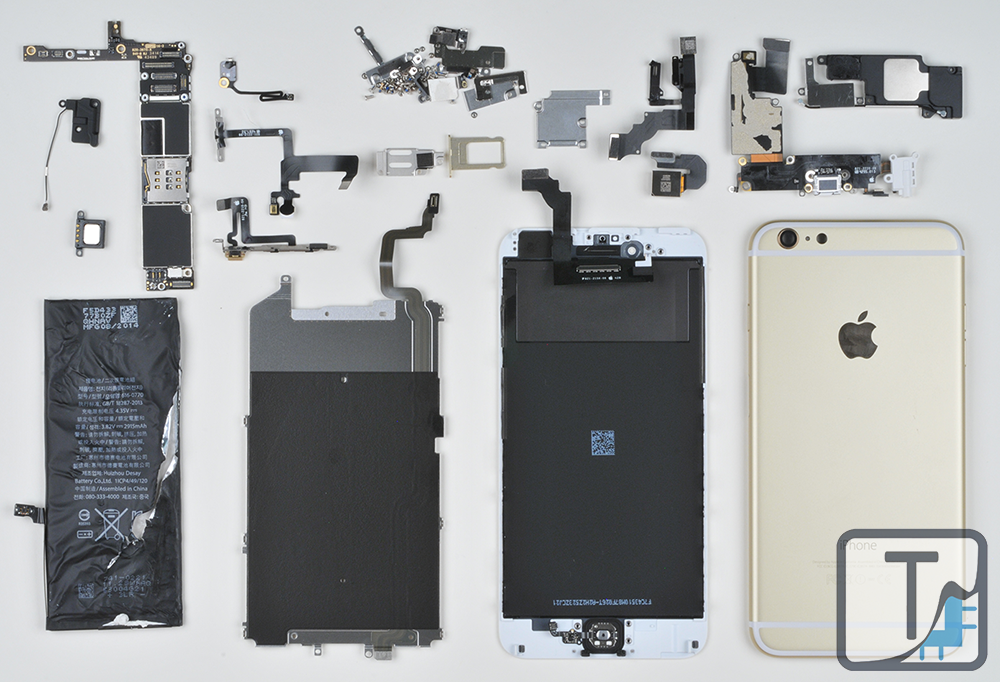
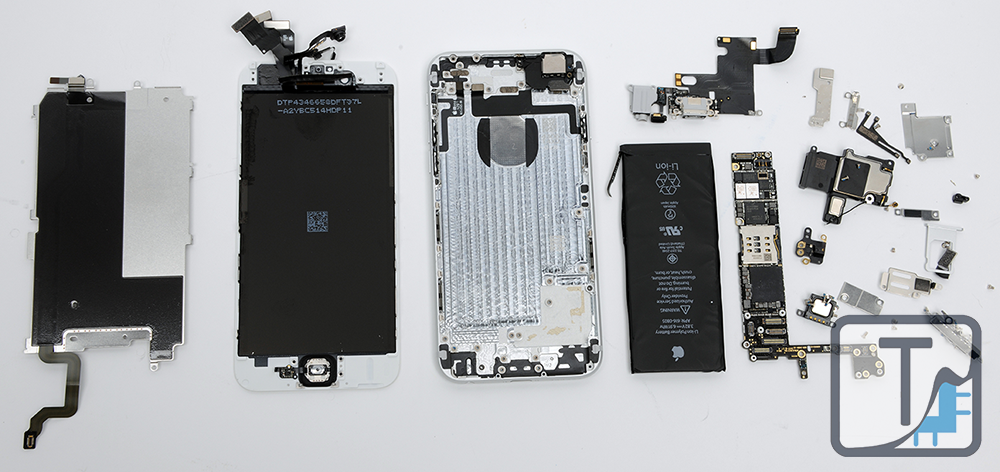
The iPhone 6 may be the most anticipated Apple handset since the original iPhone, and with good reason. In addition to the cultural impact Apple devices have been known to have, the market capitalization of certain chip manufacturers will fluctuate by millions of dollars based on their presence or absence in this device. Whatever your preferred handset ecosystem, there is no denying that this is a release of historical importance. So without further ado, we now add our own contribution to this event by letting you see what's inside the iPhone 6.
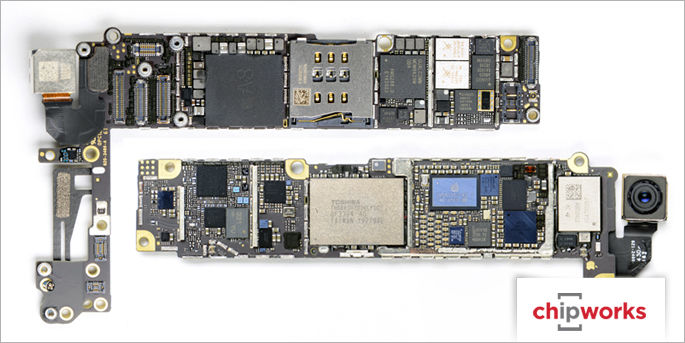
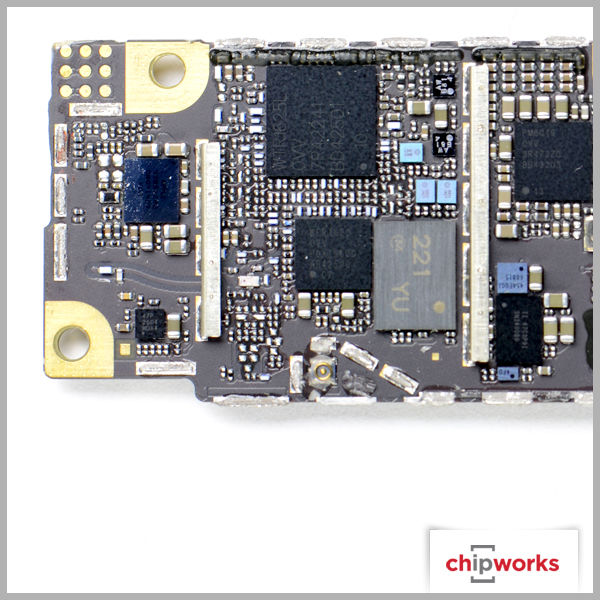
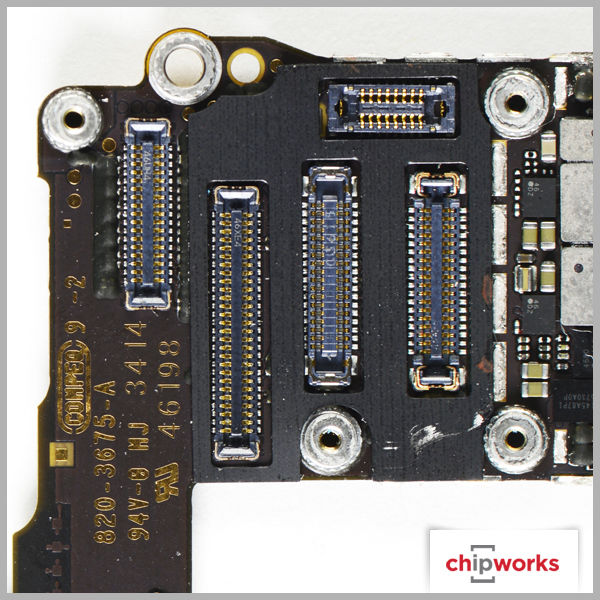
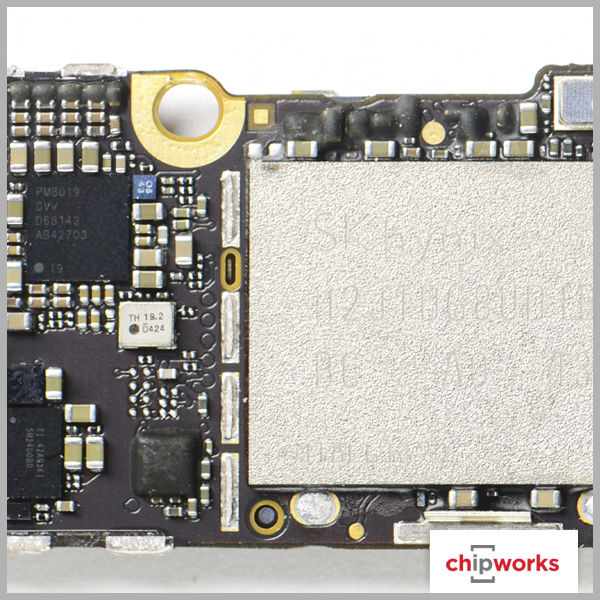
Apple iPhone 6 Board Shots
Apple iPhone 6 Plus Board Shots

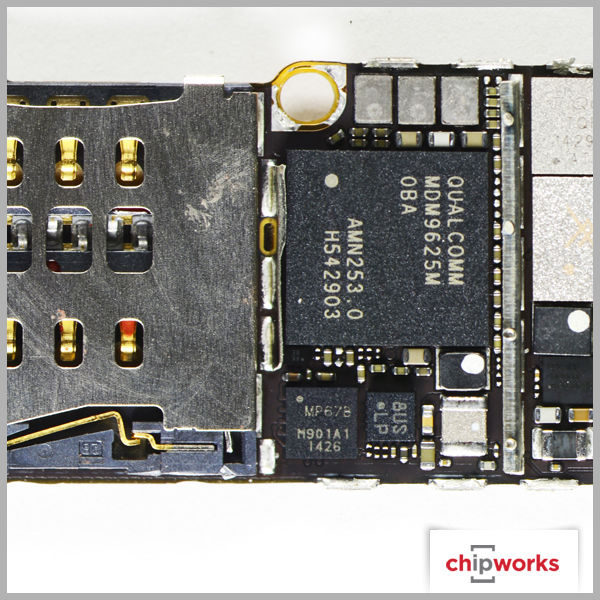
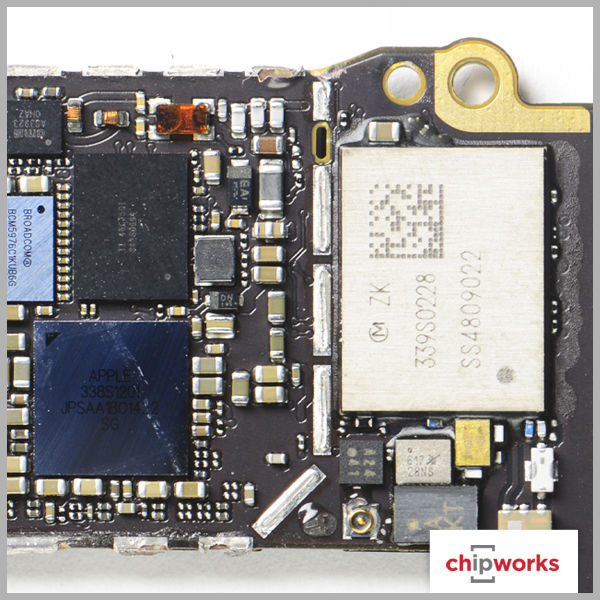
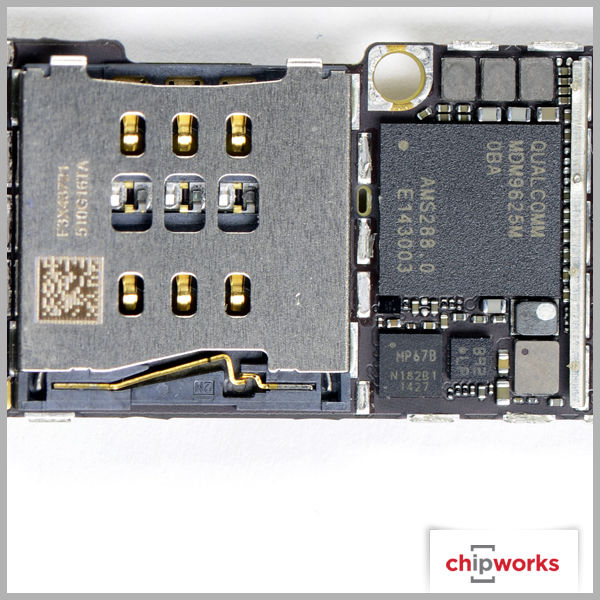
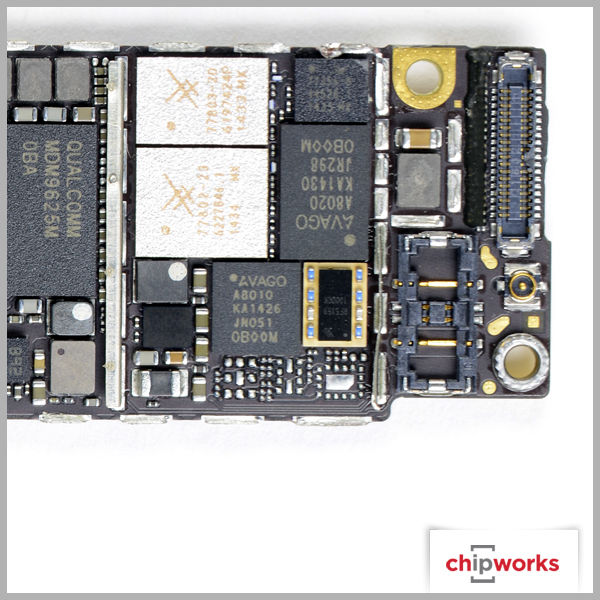
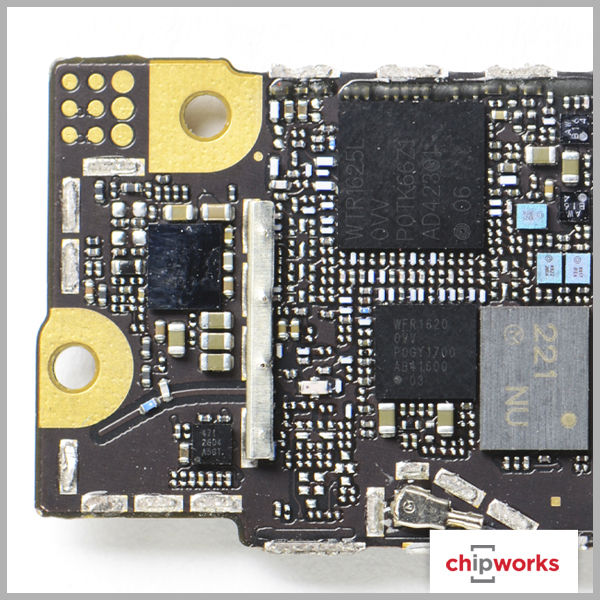
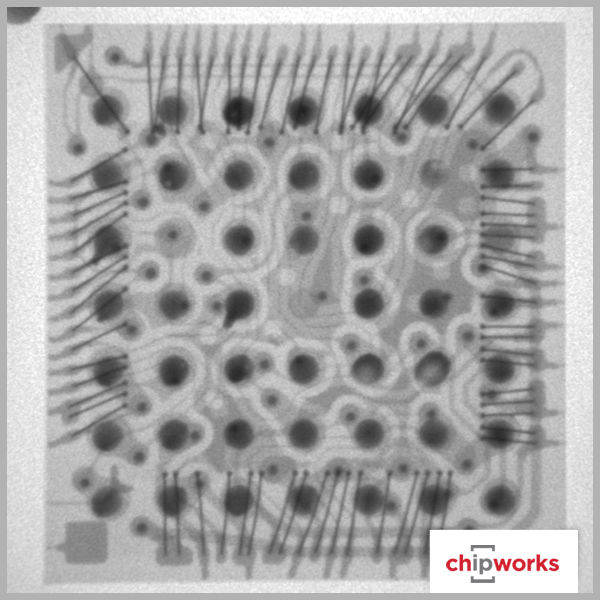
Qualcomm Gobi MDM9625M Baseband Processor
Qualcomm Gobi MDM9625M Baseband Processor
Qualcomm makes their appearance in a few places, but not as a total RF solution. The baseband support for both Apple iPhone 6 devices is from Qualcomm's Gobi Modem product line- the MDM9625M, with RF transceiver and RF receiver roles being supported by their WTR1625L and WFR1620 ICs respectively. The only other RF support we see from Qualcomm is with their power envelope tracking IC, the QFE1100. As for the other RF functions such as the RF antenna switches and power amplifiers, Apple once again uses multiple manufacturers like RFMD, Murata, Avago, and Skyworks. Based on our quick analysis, this is the same RF design strategy Apple used on the iPhone 5, iPhone 5S, and iPhone 5C.
One other notable observation - we found a 6-axis InvenSense gyroscope and accelerometer sensor. In the iPhone 5S model we had noted these functions were split between two manufacturers, STMicroelectronics and Bosch Sensortec. In the iPhone 6 Plus, STMicroelectronics was missing, replaced by the new InvenSense part while Bosch is found supporting a 3-axis MEMS accelerometer function. As we progress through the full Deep Dive, we will try to understand the need for the additional accelerometer.

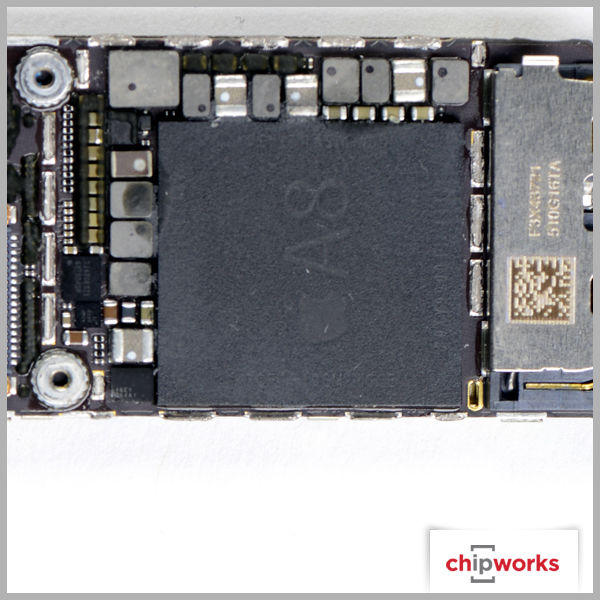
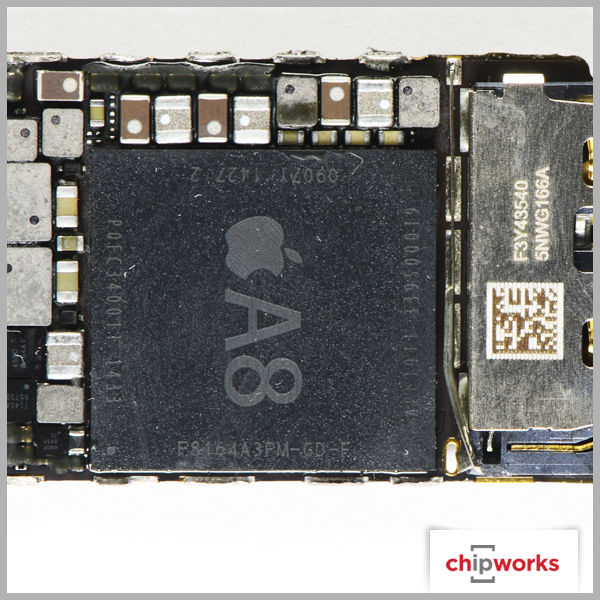
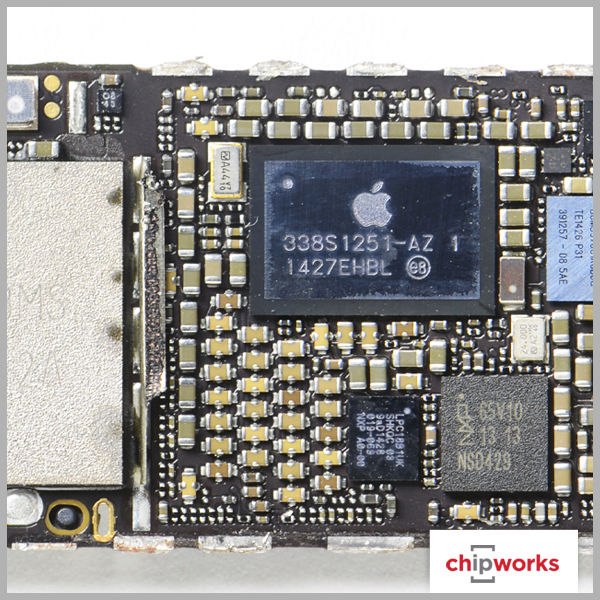
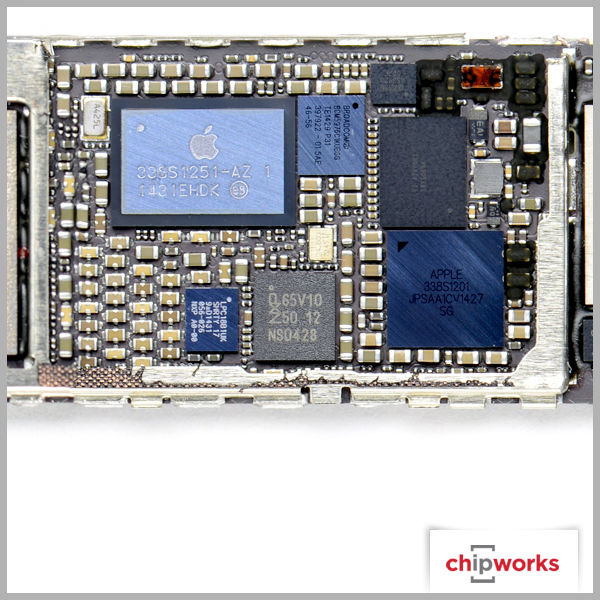
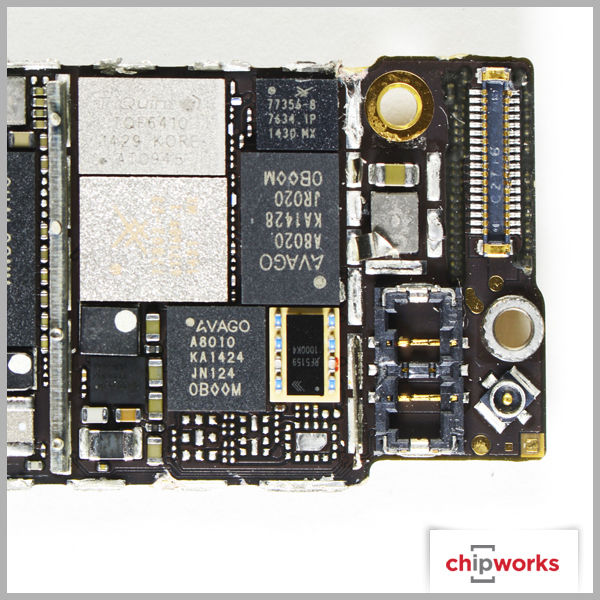
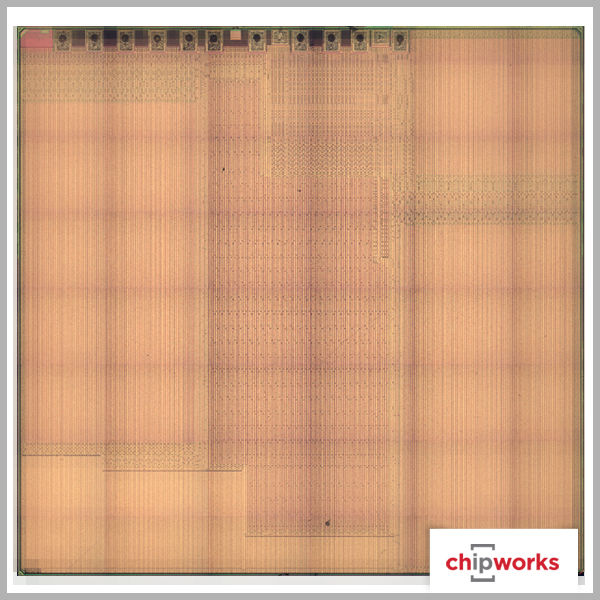
Apple A8 Processor
Apple A8 Processor
The announcement of the A8 processor was expected since Apple releases new processors simultaneously with their new phones. The A8 is smaller than its predecessor, the A7, and also has an NXP LPC18B1 M8 motion co-processor just as the A7 was supported by an M7 co-processor.
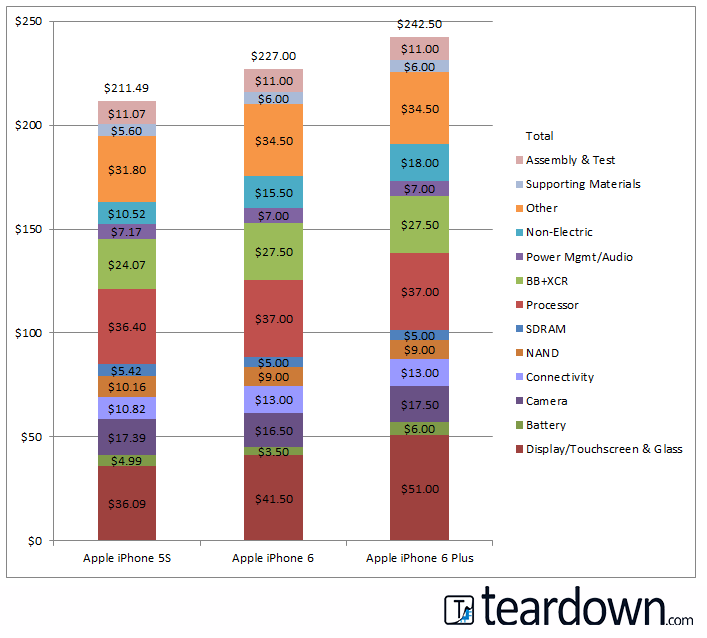
Costing
Costing
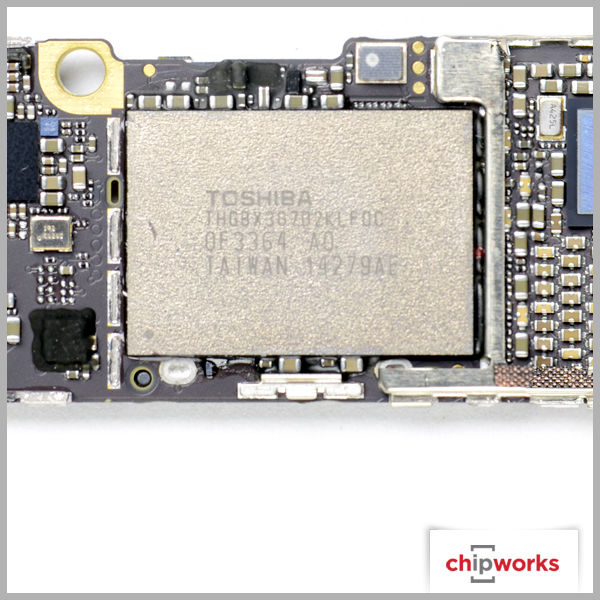
Preliminary analysis of the iPhone 6 Plus estimates it costs $242.50 USD to build - an increase of about 15% more than the iPhone 5S. The estimated combined cost of Apple's new A8 processor and Qualcomm's MDM9625M modem account for $59.50 of the preliminary CoG, while the 5.5" display / touchscreen assembly costs another estimated $51.00. For the iPhone 6 the preliminary display / touchscreen cost about $41.50 with the iPhone 6 total CoG to be approximately $227.00.
Both devices have an intricately made back enclosure which uses several pieces of extruded and machined metal work. We are estimating the cost for this piece on the larger iPhone 6 Plus to be around $15.
The increase in build cost was expected considering the larger display, expanded cellular coverage, the addition of NFC, and a larger battery.
* Costs are based off of TechInsights Quick Turn estimates. The costs are likely to be different once full teardown analysis is performed. ** NAND normalized to 32 GB units.
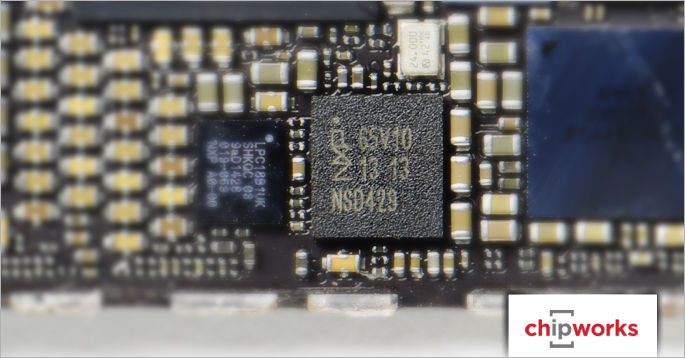
NFC Controller
NFC Controller
Based on historical package markings of NXP NFC controllers in our archive as well as leaked iPhone 6 board images, we expect the NFC controller to be NXP’s PN544, or a variant thereof. The widespread expectation that Apple will one day unlock the functionalities of NFC for functions other than Apple Pay also supports the prediction that a standard NFC controller would be used instead of a heavily customized device.
Having now depotted the 65V10 device, we can positively identify the NFC controller as the PN548, a previously unannounced variant of the PN544 and PN547 devices by NXP. Industry sources identify this as a design that was tweaked specifically for Apple by NXP. If this is true, Apple has had access to this chip for over 18 months, since the mask date (the date appearing on the die itself and indicating the year the design was finalized) is 2012. Indeed, the die markings of the PN548 vary only slightly from those of the PN547: NXP - 2012 - 7PN547V0B | NXP - 2012 - 7PN548V0C
Interestingly, a second die called “008” and sporting 2013 die markings is packaged with the PN548. However, there was no die packaged with PN547 devices we have previously seen. The 008 die shows a mysteriously dense upper metal layer. Is this the Secure Element device? Time will tell.
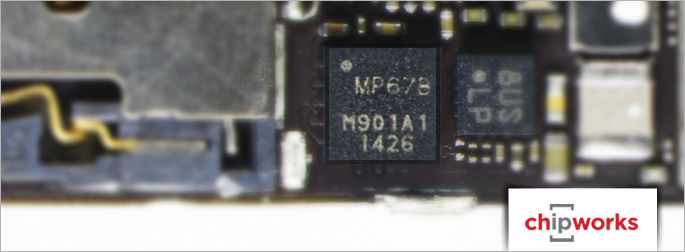
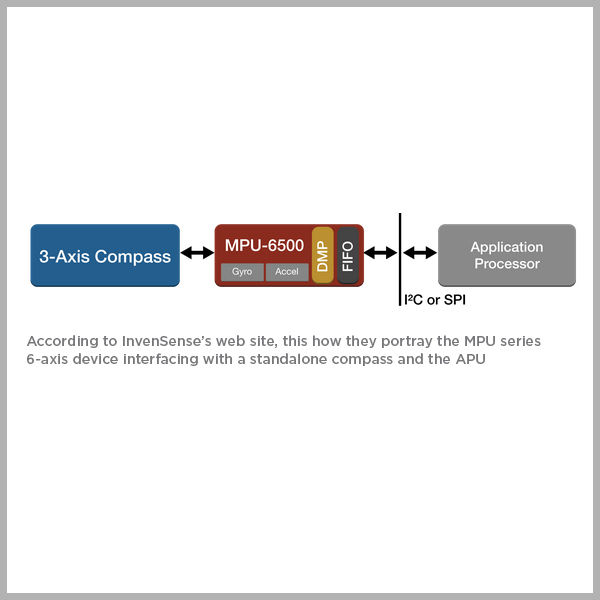
The 6-Axis Accelerometer and Gyroscope
The 6-Axis Accelerometer and Gyroscope
Another upset in the iPhone 6 Plus is the accelerometer and gyroscope. Traditionally, STMicroelectronics holds this slot(s). Today, however, InvenSense drops into this socket. This new 6-axis accelerometer and gyroscope is called the MP67B. According to InvenSense’s website, the second thumbnail above is how they portray the MPU series 6-axis device interfacing with a standalone compass and the APU.
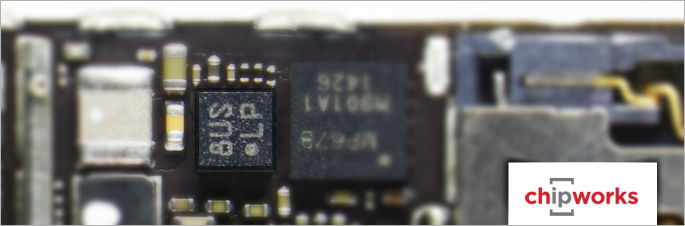
eCompass
The eCompass
The compass for past iPhones has always been a slot held by AKM Semiconductor. We have seen the AKM8963 in several Apple phone models, as well as phones from Samsung, LG, Motorola, Huawei, ZTE and others. Today we are quite puzzled. There is no AKM device obvious anywhere on the PCB, front or back. We see a six-axis InvenSense MPU7 series sensor, and next to it, we see what surely looks to be a 2 mm x 2 mm Bosch Sensortec device. Initially, we thought this to be the eCompass, but the package size and markings do not concur with standard eCompass devices on Bosch’s web site or with those we have previously observed. Now that we have done some lab work, this Bosch device looks like the BMA280 we have seen in dozens of handsets. Given this, two big questions arise: 1) Where is the compass? and 2) Why would Apple have two accelerometers? The answer is, simply, they wouldn’t do that. So why are there two accelerometers in these new products?
Update: AKM has held the eCompass slot in Apple iPhones for many generations. We were pleased to see they still hold this slot. The AKM 8963 was located under one of the glob top encapsulated devices at the extreme end of the motherboard.

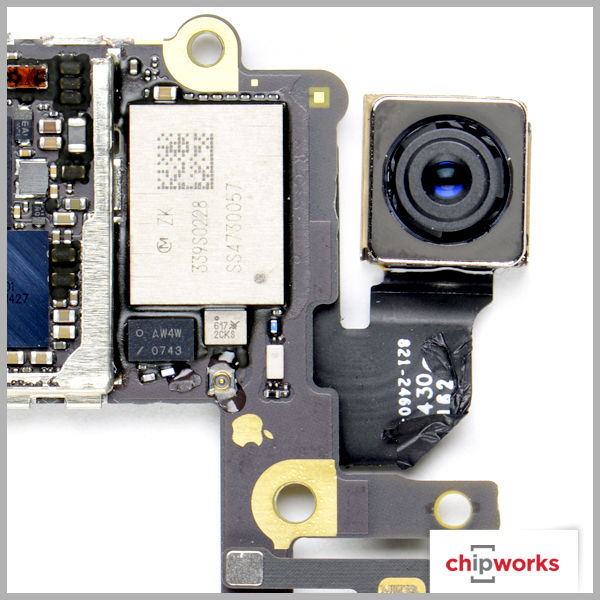
Camera Enhancement
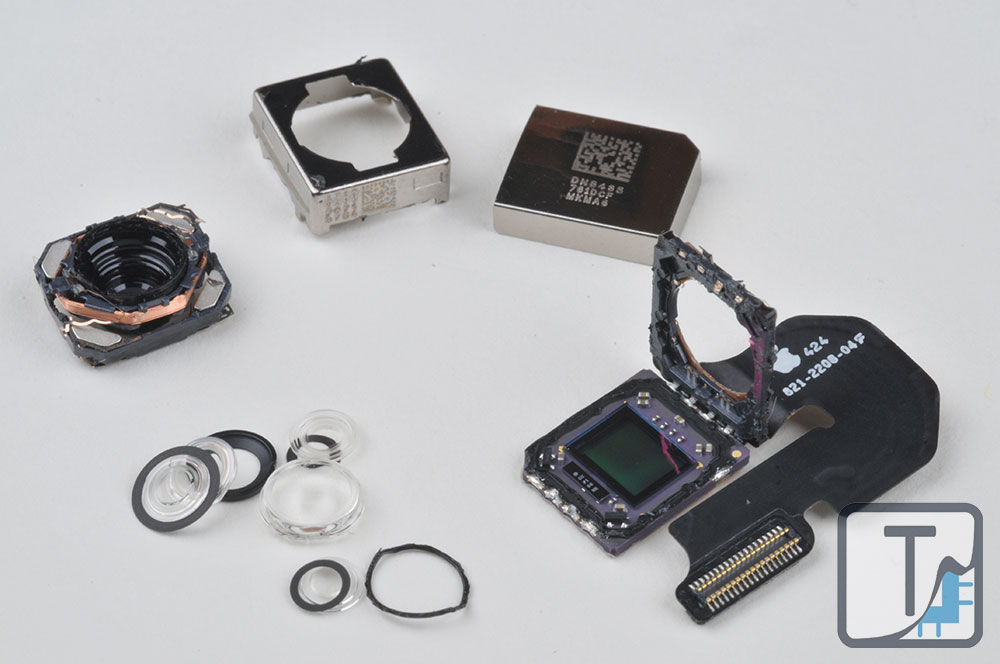
Camera Enhancement
Apple has not increased the camera size in their iPhones since the iPhone 4S. Instead, Apple decided to keep the same size 8MP rear camera for both devices with some additional camera enhancements. With the iPhone 6 Plus, they also added optical image stabilization (OIS).
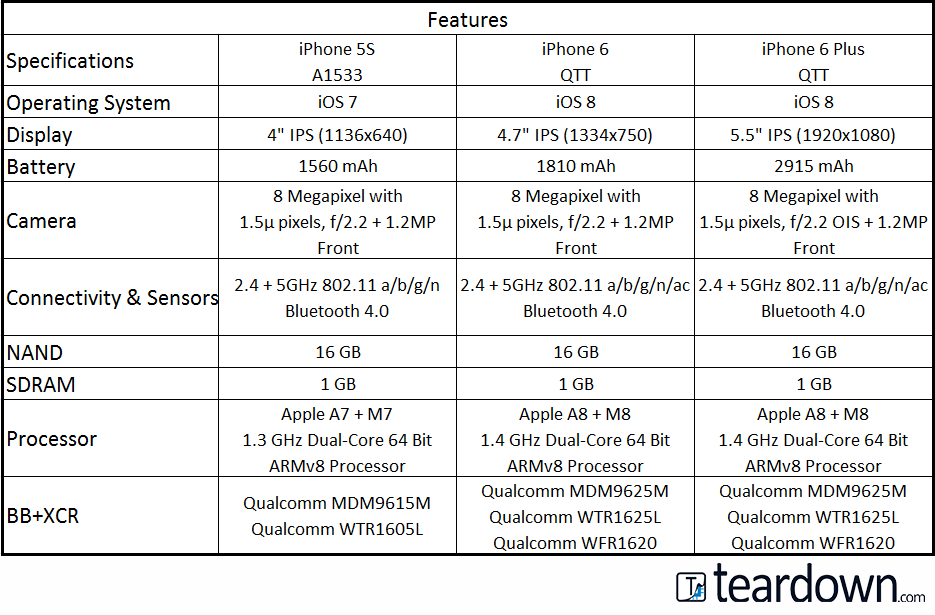
iPhone Features Comparison
Comparing Specifications: Apples to....
Samsung is Apple's largest competitor, and both are facing tough competition from Chinese OEMs like Xiaomi. We are scheduled to do further a quick turn analysis on the Samsung Galaxy Note 4 to be released in October as well as trying to coordinate the same for the Xiaomi Mi4 LTE phone once it is release.