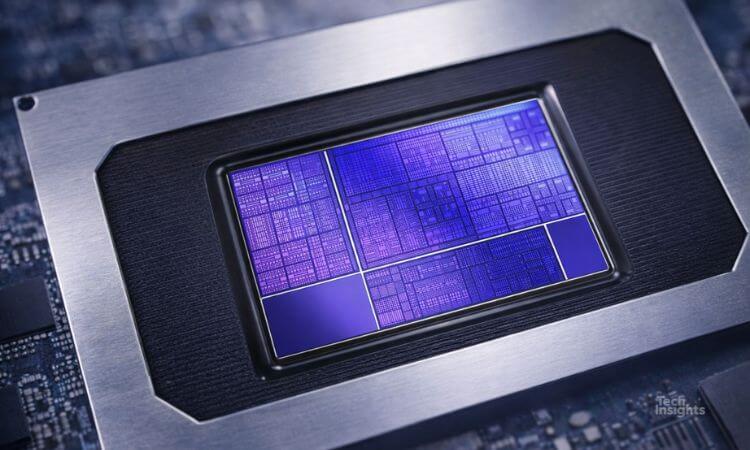
AMD’s Area Efficiency Beats Intel’s
TechInsights’ floorplan analysis of desktop-PC processors quantifies the size difference among AMD and Intel CPUs.

Joseph Byrne
For the Ryzen 7000 series of desktop-PC processors, AMD raised the chips’ power limits and updated its CPU to Zen 4. Taking advantage of a 5 nm TSMC process and focusing on integer performance, the company produced a core that delivers high throughput in an economical, compact physical design.
Intel has combined two CPU types in its PC processors. The Raptor Cove CPU in its most recent Raptor Lake design achieves a slightly higher clock speed than Zen 4 in the less-advanced Intel 7 process through an aggressive microarchitecture and circuit design. It’s therefore far less area efficient. To raise overall throughput of its Raptor Lake PC processors, Intel supplements Raptor Cove with many Gracemont CPUs. Although a fraction of Raptor Cove’s size, they aren’t much smaller than Zen 4 owing to AMD’s process-technology advantage.
Our evaluation is based on TechInsights’ teardown and floorplan analysis of the Ryzen 7950X compute die and the Core i9-13000K processor. We also collected Geekbench performance and Prime 95 power data from NotebookCheck.
Free Newsletter
Get the latest analysis of new developments in semiconductor market and research analysis.
Subscribers can view the full article in the TechInsights Platform.
You must be a subscriber to access the Manufacturing Analysis reports & services.
If you are not a subscriber, you should be! Enter your email below to contact us about access.